Low-Code Development: Trends and Predictions for 2026
AI-powered development, intelligent automation, cross-platform UI/UX and the rise of citizen developers – a look at how low-code will reshape business systems in the next few years.

DevLab Blog explores how modern companies design flexible, extensible ERP systems using open technologies, declarative business logic and low-code approaches. Practical notes, experiments and implementation patterns for teams that want to avoid vendor lock-in and build systems that actually fit their business.
AI-powered development, intelligent automation, cross-platform UI/UX and the rise of citizen developers – a look at how low-code will reshape business systems in the next few years.

How visual tooling, reusable components and hybrid development models make it easier for organisations to deliver modern applications faster, with fewer technical barriers and lower cost.

How low-code is evolving in 2025: AI integration, automation, UX improvements, security and the rising role of citizen developers across different industries.

Why low-code platforms are becoming a strategic choice in 2025: how they differ from classic RAD, what drives adoption, and how they impact time-to-market, costs and agility.

The low-code market is growing from $22.5B to a projected $94B and is changing how software is built: we compare low-code with no-code, explain how the process works and what benefits it gives in speed, cost and flexibility.

What low-code platforms are, which principles they are built on, where they bring the most value and what trends – from AI and hybrid development to serverless and compliance – will define their future.

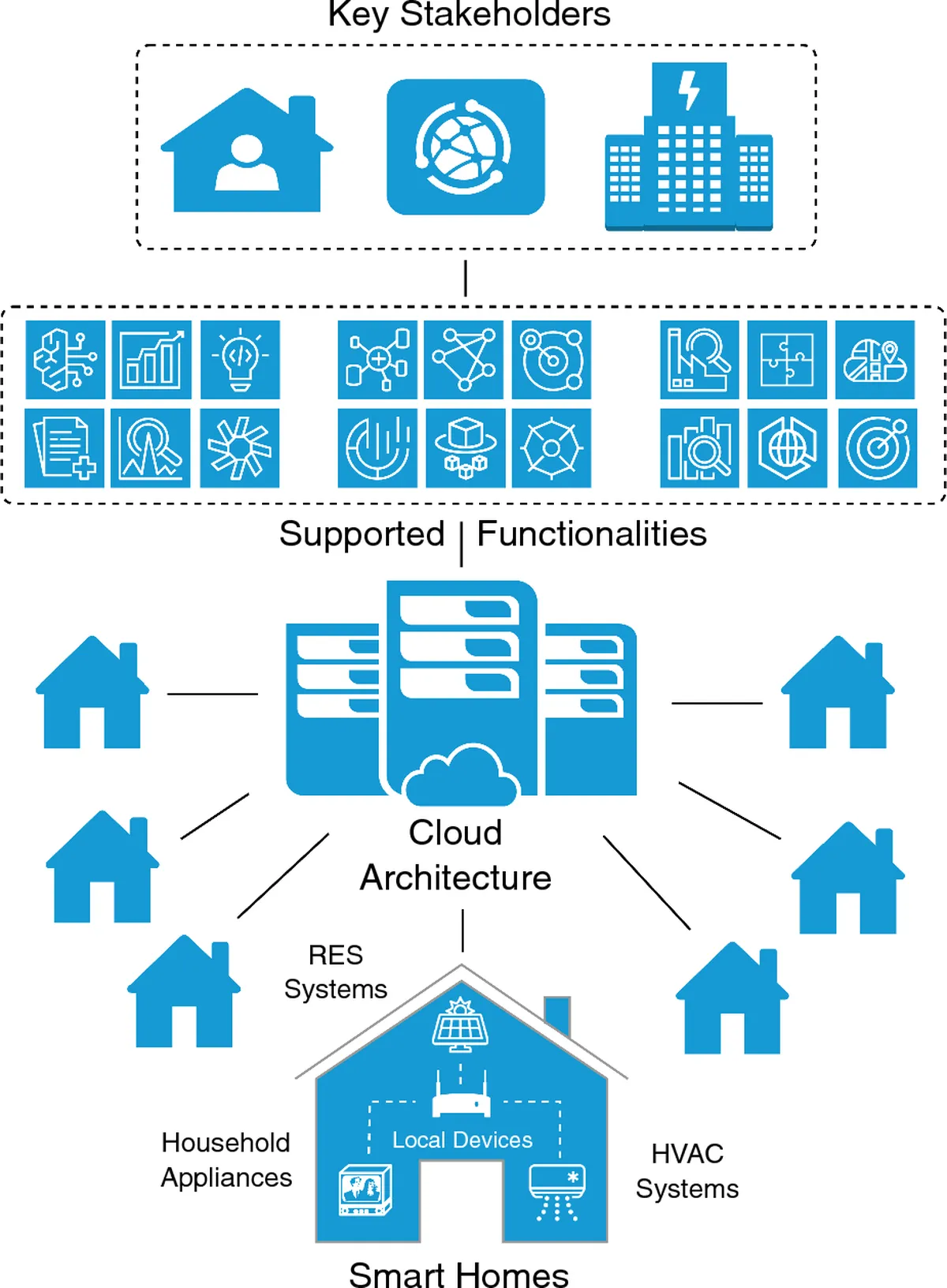
Modular architectures, declarative models and open ecosystems are reshaping the ERP landscape. Companies are rethinking classic suites in favour of API-first, flexible stacks with transparent costs and faster innovation cycles.
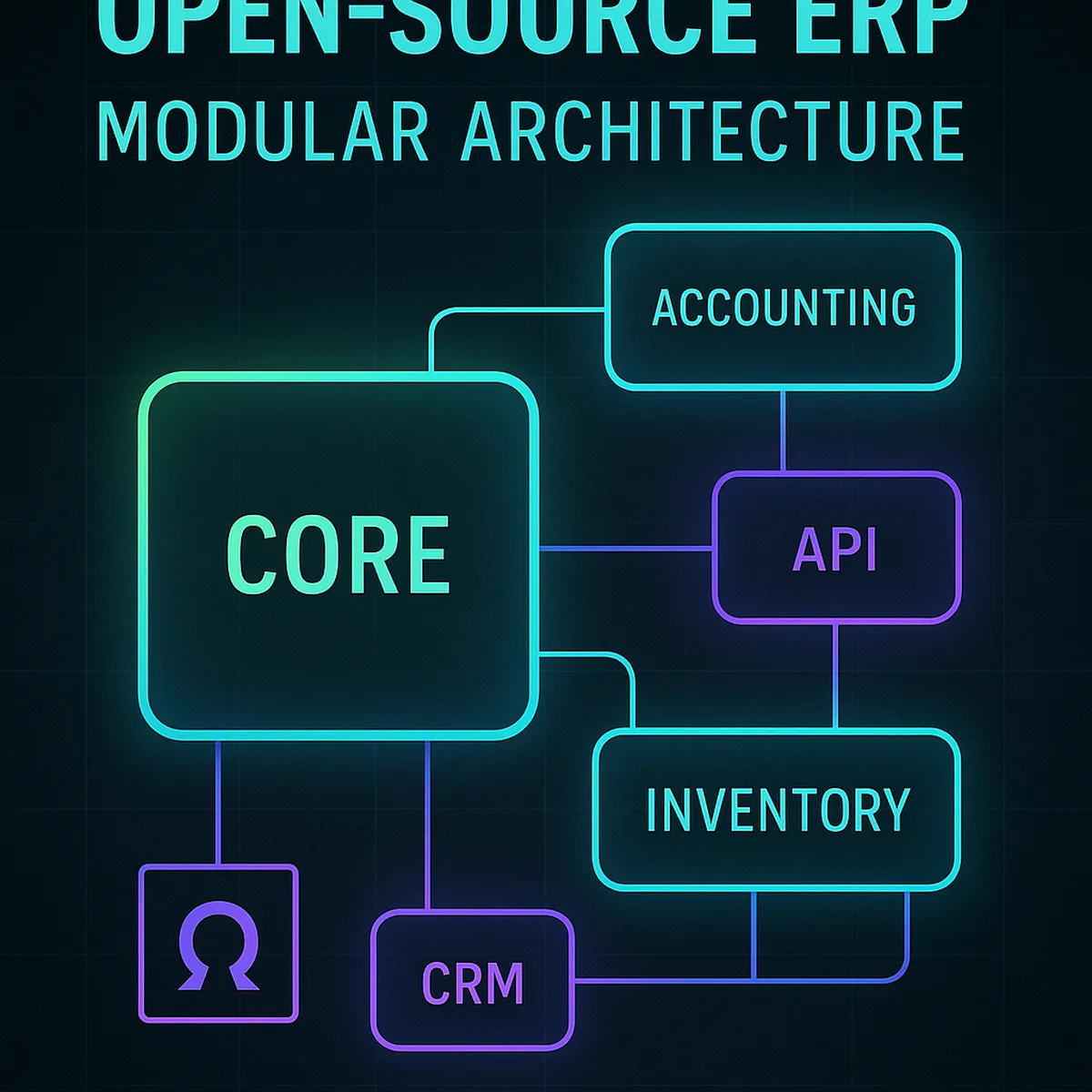
How to structure an ERP core into modules, keep integrations clean and avoid another generation of tightly coupled “big ball of mud” systems.
A practical approach to helping analysts, domain experts and future citizen developers understand ERP logic, automation patterns and modern tooling – without a software engineering background.

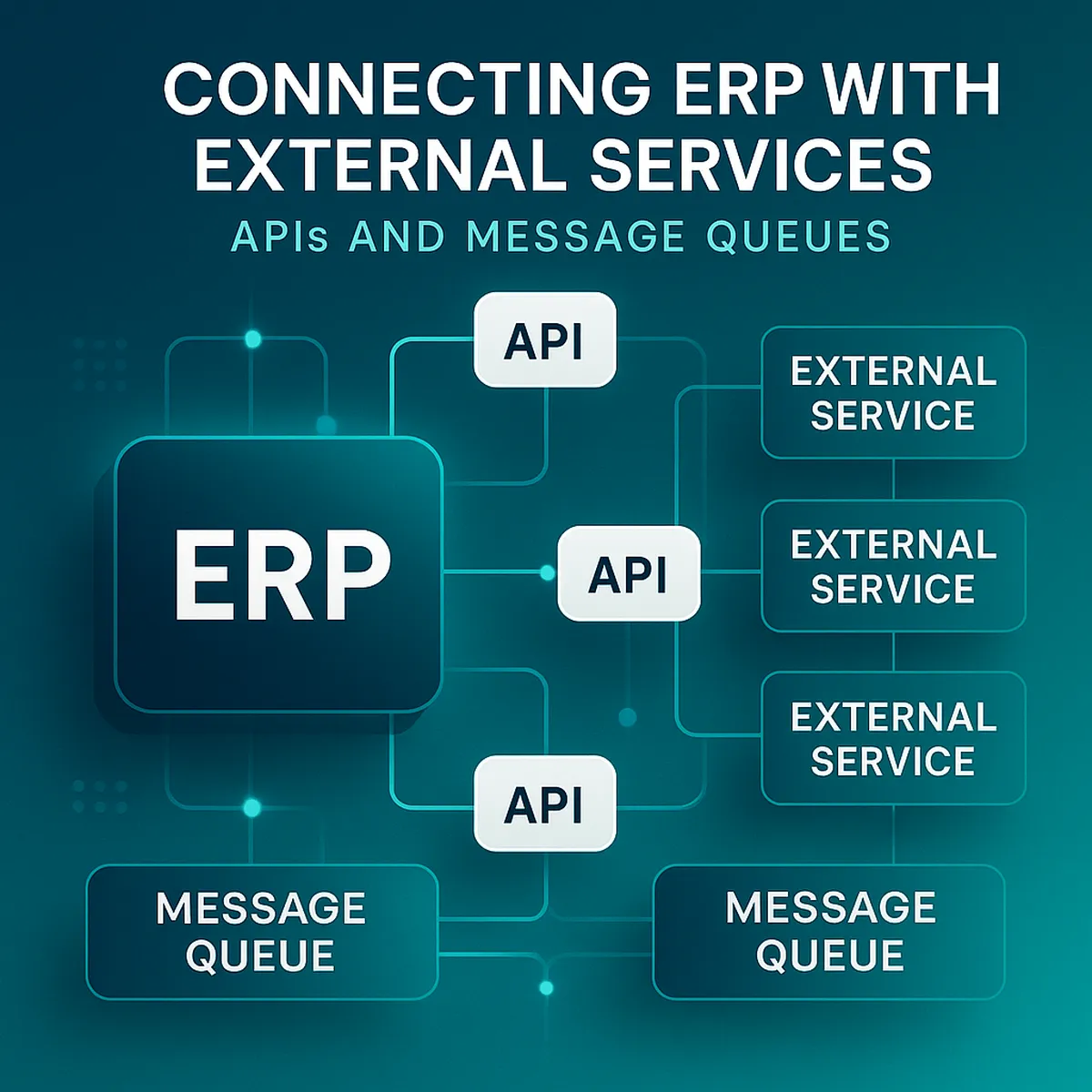
A practical guide to linking ERP systems with payments, CRM, WMS and custom services — using REST APIs, message queues and event-driven workflows without compromising stability.
Practical patterns for adding low-code modules on top of an existing ERP — from small approval workflows to side-car apps that keep the core clean while still delivering what the business needs.
What KSeF really changes, key deadlines for 2026 and how low-code platforms help Polish companies integrate e-invoicing into their ERP and workflows without huge IT budgets.

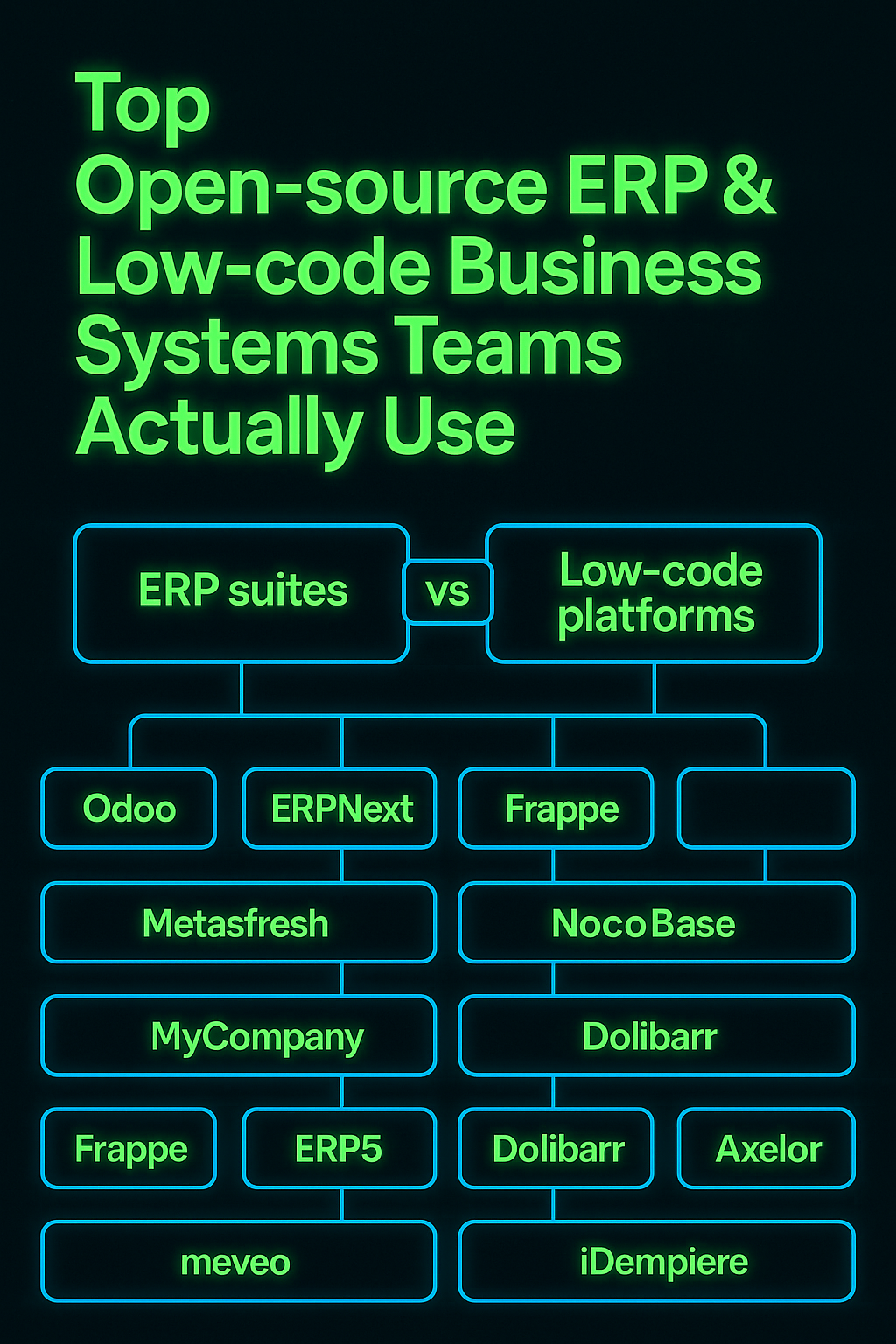
A practical overview of 12 open-source ERP and low-code platforms — what they’re good at, where they struggle, and how to choose the right approach when off-the-shelf ERP doesn’t fit.
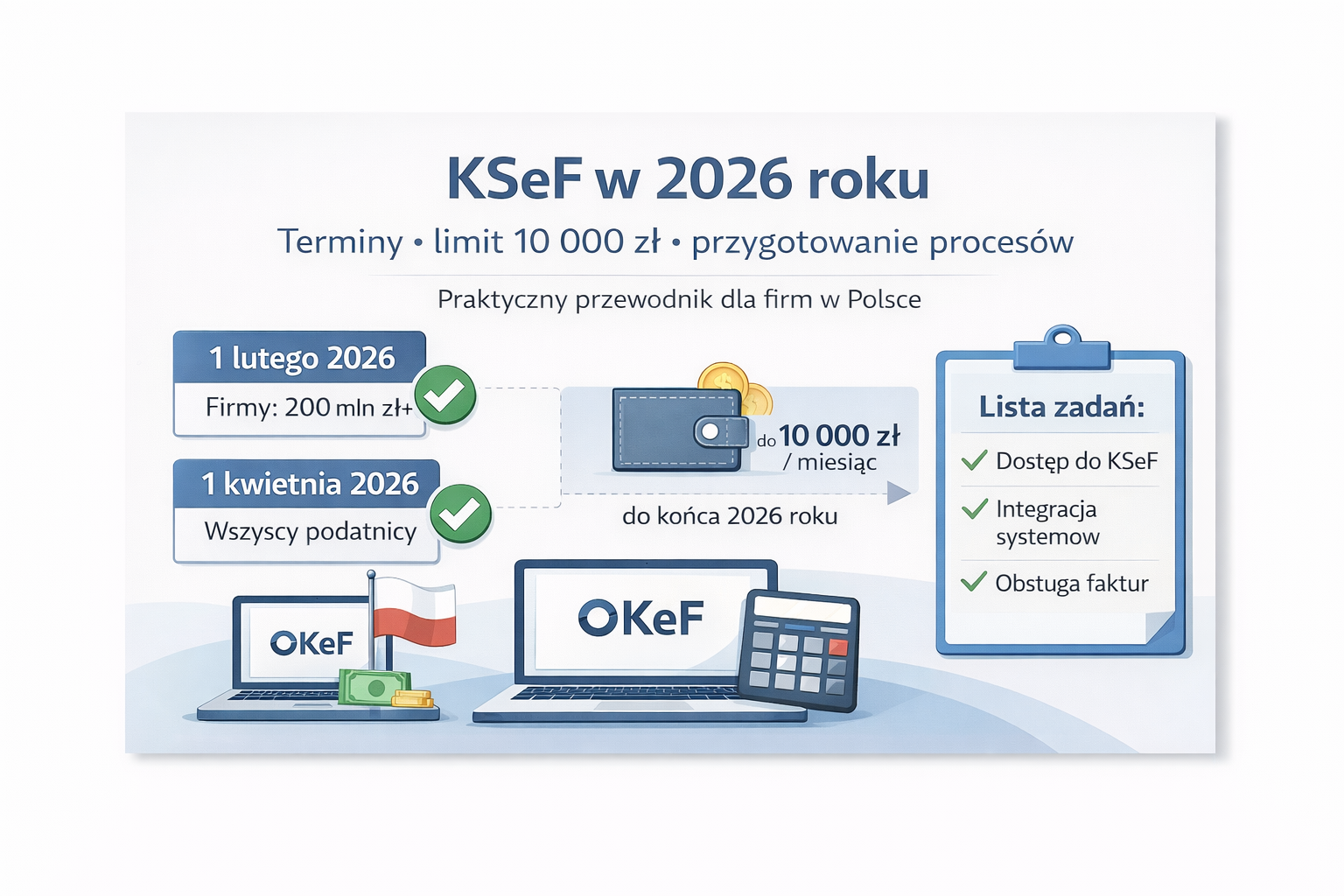
When KSeF becomes mandatory, how the 10,000 zł exception works until the end of 2026, and what companies actually need to prepare in processes and systems — without marketing or vague explanations.
KSeF rarely breaks on day one — the real pain starts later: rejected invoices, manual retries, drifting ERP data and corrections that destroy the workflow. Here’s a practical checklist + a 30/60/90-day stabilization plan.

Most ERP failures don’t happen during implementation — they happen later, when the business changes. This is a practical architecture review with real mini-cases and honest comparisons (no vendor worship).